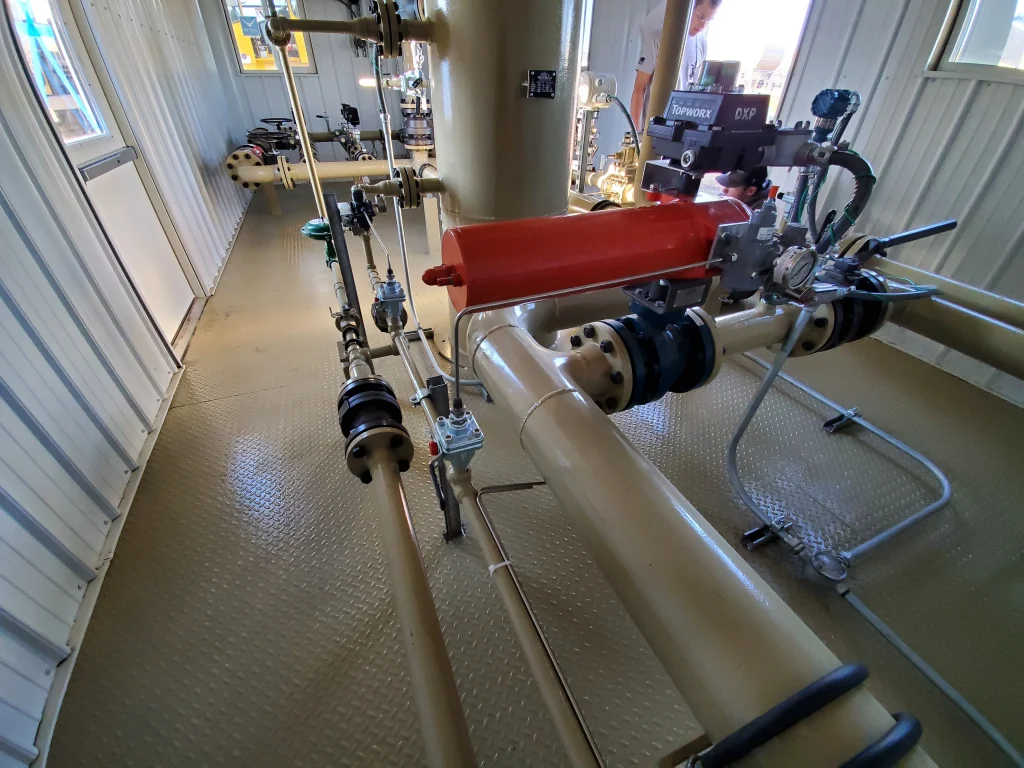
Introduction of ASME pressure vessel certification
In the world of industrial equipment, safety and quality are paramount. ASME pressure vessel certification is a crucial aspect of ensuring that pressure vessels, which are ubiquitous in various industries, meet rigorous standards for safety, reliability, and performance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of ASME pressure vessel certification, its importance, and what it entails.
Understanding ASME
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) is a globally recognized nonprofit organization that sets the standards and codes for a wide range of mechanical engineering practices, including pressure vessels. ASME’s Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) is the backbone of these standards, serving as the go-to resource for engineers and manufacturers around the world.
What is a Pressure Vessel?
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure. They are employed in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and many others. Pressure vessels come in various shapes and sizes, from small storage tanks to massive industrial reactors, and they play a vital role in modern manufacturing and energy production.
Importance of ASME Pressure Vessel Certification
- Safety: The primary reason for ASME certification is to ensure the safety of personnel, the environment, and the surrounding community. ASME standards help prevent catastrophic failures, leaks, and explosions by setting strict design, fabrication, and inspection requirements.
- Compliance: ASME certification is often a legal requirement in many jurisdictions. Manufacturers must comply with these standards to avoid fines, penalties, and legal liabilities.
- Quality Assurance: ASME certification signals a commitment to quality. It assures customers and stakeholders that the pressure vessels they purchase or operate have been built and inspected to the highest standards.
ASME Pressure Vessel Certification Process
- Design and Engineering: The process begins with the design and engineering phase. Engineers must adhere to ASME BPVC requirements when designing pressure vessels. This includes calculations for material selection, thickness, and stress analysis.
- Fabrication: During fabrication, manufacturers follow ASME guidelines for materials, welding, and construction. Welders must be certified, and the welding processes must conform to ASME standards.
- Inspection and Testing: Rigorous inspections and tests are conducted to verify compliance. These may include non-destructive testing (e.g., X-ray, ultrasonic), hydrostatic testing, and visual inspections.
- Documentation: Thorough documentation of the design, fabrication, and testing processes is required for ASME certification. This includes detailed records of materials used, welding procedures, and inspection reports.
- ASME Stamp: Upon successful completion of all requirements, pressure vessels receive an ASME stamp, indicating compliance with the BPVC. The type of stamp (e.g., U-Stamp, R-Stamp) depends on the specific application and usage of the vessel.
Common Types of ASME Pressure Vessel Certifications
- U-Stamp: The U-Stamp is one of the most common certifications and is used for pressure vessels designed for general use. It covers a wide range of applications and is often required for items like storage tanks, heat exchangers, and air receivers.
- R-Stamp: The R-Stamp is specific to pressure vessel repairs and alterations. If a pressure vessel undergoes repairs or modifications, it must be certified to meet ASME standards to ensure its continued safety and reliability.
- S-Stamp: The S-Stamp is for the manufacture and assembly of power boilers. Power boilers are typically found in power plants and are used to generate steam for electricity generation.
- A-Stamp: The A-Stamp is for pressure vessels that are manufactured by brazing. Brazing is a joining process that uses a filler metal to create a bond between materials. ASME certification ensures that brazed pressure vessels meet safety and quality standards.
- H-Stamp: The H-Stamp is for heating boilers used in heating systems. These boilers are common in residential, commercial, and industrial heating applications.
- PP-Stamp: This certification is for pressure vessels used in petrochemical and chemical processes. It ensures that these vessels are designed and manufactured to withstand the often corrosive and high-temperature environments of these industries.
- HLW-Stamp: The HLW-Stamp is specific to nuclear power applications. Pressure vessels used in nuclear reactors and related systems must meet exceptionally stringent safety and quality standards.
Maintaining ASME Certification
Once a pressure vessel is certified, it is essential to maintain that certification. Regular inspections, maintenance, and compliance with ASME guidelines are necessary to ensure ongoing safety and performance. Failure to do so could result in decertification, fines, or even legal consequences.
Challenges in ASME Pressure Vessel Certification
While ASME pressure vessel certification is essential for safety and quality assurance, it comes with its own set of challenges for manufacturers and operators:
- Complexity: The ASME BPVC is a comprehensive and intricate set of codes and standards that require a deep understanding of engineering principles. Compliance can be challenging and may require specialized expertise.
- Cost: Achieving ASME certification can be expensive. Manufacturers must invest in materials, equipment, personnel training, and inspection processes that meet ASME requirements. However, the long-term benefits in terms of safety and reputation often outweigh the initial costs.
- Documentation: Strict documentation and record-keeping are essential for certification. Manufacturers must maintain extensive records of design, fabrication, inspection, and testing processes. This can be a time-consuming task, but it is crucial for compliance.
- Regulatory Variations: ASME standards are widely adopted, but regulatory
requirements may vary from one jurisdiction to another. Manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of international, national, and local regulations to ensure compliance. - Continuous Updates: ASME periodically updates its codes and standards to reflect technological advancements and industry best practices. Manufacturers must stay up-to-date with these changes to maintain certification.
- Global Compliance: For international manufacturers, ensuring compliance with ASME standards while meeting the requirements of other regulatory bodies can be a complex task. Achieving certification that satisfies multiple global standards may be necessary for export purposes.
- Pressure Equipment Directive (PED): In Europe, the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) is often used in conjunction with ASME certification. Manufacturers exporting to Europe must ensure that their products meet both ASME and PED requirements.
The Future of ASME Pressure Vessel Certification
As technology advances and industries evolve, the future of ASME pressure vessel certification is likely to see several developments:
- Digitalization: The certification process may become more digitally integrated, with manufacturers using advanced software and tools for design, simulation, and documentation. Digital twins and augmented reality may enhance inspection and maintenance processes.
- Materials Innovation: Innovations in materials science may lead to the development of new materials that offer improved strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. These materials will need to be incorporated into ASME standards to ensure safe usage.
- IoT and Sensors: The Internet of Things (IoT) and sensor technology may play a significant role in monitoring pressure vessels in real-time. Smart pressure vessels could detect issues and provide data for predictive maintenance, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- International Harmonization: Efforts to harmonize international standards and regulations for pressure vessels may continue, simplifying compliance for manufacturers operating in multiple countries.
- Environmental Considerations: As environmental concerns grow, pressure vessel certification may place more emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency. Standards may evolve to encourage the development of eco-friendly pressure vessels.
- Safety Innovations: Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning may be used to analyze pressure vessel data and predict potential safety issues before they occur, further enhancing overall safety.
- Globalization: ASME standards may continue to gain global recognition and adoption as industries become more interconnected and reliant on international trade.
- Customization and Specialized Certifications: In the future, industries may demand more specialized pressure vessels tailored to unique applications. ASME may adapt by offering more customized certification processes to accommodate these diverse needs. This could include niche certifications for emerging technologies like hydrogen storage or carbon capture.
- Energy Transition: As the world shifts toward cleaner energy sources and carbon reduction, ASME pressure vessel certification may expand to cover innovations in renewable energy storage and transportation, such as high-pressure hydrogen storage tanks or advanced battery technologies.
- Cybersecurity: With the increasing connectivity of industrial equipment, cybersecurity will become a growing concern. ASME may develop guidelines and standards to ensure the cybersecurity of pressure vessels, protecting them from digital threats and vulnerabilities.
- Data-Driven Certification: The collection and analysis of real-time data from pressure vessels may become a standard practice. This data-driven approach could enhance safety by providing insights into performance, wear and tear, and maintenance needs.
- Global Collaboration: In an increasingly interconnected world, collaboration between international standards organizations will continue to grow. ASME may work closely with other standards bodies to harmonize regulations and streamline the certification process for global manufacturers.
- Sustainability Standards: As environmental awareness intensifies, ASME may incorporate sustainability metrics into certification processes, encouraging pressure vessel designs that minimize carbon footprints, waste, and resource usage.
- Education and Training: The need for skilled professionals in pressure vessel design, manufacturing, and inspection will persist. ASME may expand its educational offerings and training programs to meet this demand and ensure that certified professionals remain up-to-date with evolving technology.
The Role of AI and Automation:
In the future, artificial intelligence (AI) and automation will likely play a significant role in ASME pressure vessel certification. AI algorithms can assist in the analysis of design and inspection data, potentially identifying patterns or anomalies that human inspectors might miss. Automation can streamline the inspection process, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of human error.
Blockchain for Transparency:
Blockchain technology may find applications in ASME certification by providing an immutable and transparent record of a pressure vessel’s history. This can enhance trust and traceability in the supply chain, ensuring that all components and processes adhere to ASME standards.
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing:
Innovations in advanced materials like composites, nanomaterials, and additive manufacturing will require ASME to adapt and develop standards that address these cutting-edge technologies. Certification processes may need to consider unique properties and fabrication techniques associated with these materials.
Environmental Impact Assessment:
In response to global environmental concerns, ASME certification may evolve to include assessments of a pressure vessel’s environmental impact. This could involve evaluating the carbon footprint, energy efficiency, and sustainability of pressure vessels as part of the certification process.
Global Supply Chains:
As supply chains become increasingly globalized, ASME certification may involve more rigorous assessments of suppliers and subcontractors to ensure compliance with ASME standards at every stage of production.
Resilience and Disaster Preparedness:
Given the growing frequency and intensity of natural disasters and climate-related events, ASME standards may evolve to include criteria for pressure vessels to withstand extreme conditions, ensuring the resilience of critical infrastructure.
Education and Certification of Inspectors:
ASME will continue to play a vital role in the education and certification of inspectors and engineers. Training programs will adapt to incorporate the latest technologies and methodologies, ensuring that qualified professionals are equipped to meet evolving industry needs.
Public Awareness and Advocacy:
ASME may engage in more proactive public awareness campaigns to highlight the importance of ASME-certified pressure vessels in ensuring public safety and environmental protection. Advocacy efforts may also focus on promoting policies that support the adoption of ASME standards globally.
Collaborative Research and Development:
ASME may foster greater collaboration between industry, academia, and research institutions to drive innovation in pressure vessel design and manufacturing. This collaboration can lead to the development of more efficient and sustainable pressure vessels, incorporating the latest advancements in materials, processes, and technologies.
Evolving Safety Standards:
Safety will always be paramount in pressure vessel certification. ASME may continuously evolve safety standards to address emerging risks and challenges, such as those posed by new materials, operating conditions, or environmental factors. These standards will continue to ensure that pressure vessels meet the highest safety requirements.
Incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML algorithms may be integrated into the certification process to enhance predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and risk assessment. These technologies can help identify potential issues before they become critical, improving overall safety and reliability.
Green Technologies and Sustainability:
Pressure vessel certification may increasingly focus on sustainable practices and green technologies. This includes certifying pressure vessels used in renewable energy applications, carbon capture and storage, and other environmentally friendly processes.
Cybersecurity Integration:
As pressure vessels become more interconnected through the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), cybersecurity measures will become integral to certification. ASME may develop guidelines for safeguarding pressure vessels against cyber threats and ensuring data integrity.
Enhanced Communication and Reporting:
The reporting and communication of certification data may become more standardized and accessible, allowing stakeholders to easily verify the compliance and history of pressure vessels. This transparency can improve trust and accountability.
Global Standardization:
ASME may continue to work towards global standardization and harmonization of pressure vessel certification requirements. This will facilitate international trade and ensure consistency in safety and quality across borders.
Sustainable Practices:
Pressure vessel certification may include criteria related to sustainable manufacturing processes, waste reduction, and responsible sourcing of materials. This aligns with the growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility and environmental stewardship.
Resilience and Disaster Preparedness:
In an era of increasing climate-related challenges, ASME certification may place more emphasis on pressure vessels’ ability to withstand extreme weather events and natural disasters, contributing to the resilience of critical infrastructure.
Need a reliable partner?
Red River specializes in the design and manufacturing of pressure vessels. We also fabricate related items such as prefabricated spools and skid packages.
Reach Out to us today and experience the Red River difference. Where American Made and American Values come together, we care more.
FAQ: ASME Certification and Quality Assurance
What is ASME certification, and why is it important for pressure vessels?
ASME certification refers to the approval process that ensures pressure vessels are designed, fabricated, inspected, and tested under the standards set by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). It is crucial for pressure vessels because it signifies that the equipment meets the highest safety and quality standards, reducing the risk of failures and accidents in operations.
How does a manufacturer obtain ASME certification for pressure vessels?
A manufacturer obtains ASME certification for pressure vessels by following the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC) guidelines throughout the design, fabrication, and inspection processes. This involves submitting designs for approval, undergoing rigorous inspections by ASME-certified inspectors, and ensuring all materials and manufacturing processes meet or exceed ASME standards. Successful completion of these steps results in the issuance of an ASME certification mark.
What are the benefits of using ASME-certified pressure vessels?
The benefits of using ASME-certified pressure vessels include enhanced safety due to adherence to proven engineering standards, improved reliability and performance, potential for reduced insurance costs, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. ASME certification also facilitates the global acceptance of pressure vessels, as it is widely recognized as a benchmark for quality and safety.
Can a pressure vessel lose its ASME certification, and under what circumstances?
Yes, a pressure vessel can lose its ASME certification if modifications are made without proper notification and re-inspection by an ASME-certified inspector, if it fails to pass periodic inspections, or if it is found to be in violation of the ASME BPVC standards. Maintaining certification requires adherence to ASME guidelines throughout the vessel’s operational life.
What is the difference between ASME certification and ASME stamping?
ASME certification is the process by which a manufacturer is recognized as capable of designing and fabricating pressure vessels according to ASME standards. An ASME stamp, or the “U” stamp for pressure vessels, is a specific mark that is applied to the vessel itself, indicating that the individual vessel has been manufactured in compliance with ASME BPVC requirements.
Related Blog Post

Understanding Different Types of Failure in Pressure Vessels

The Most Common Type of Pressure Vessel Used in Industry


Understanding Adsorption Air Dryers

Types of Failure in Pressure Vessels
No pillar keyword set for this post.