Distinctions Between Tanks and Pressure Vessels
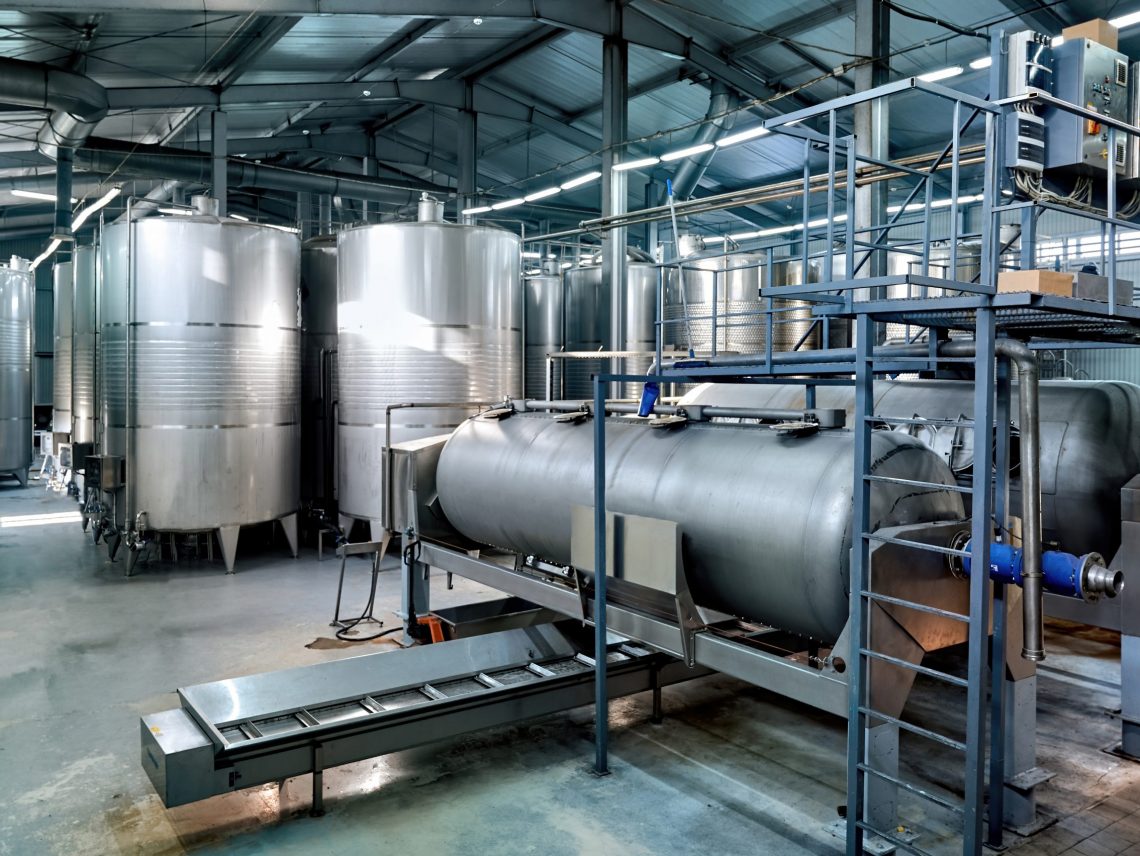

Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the difference between a tank and a pressure vessel?
In the realm of industrial equipment and systems, it’s essential to differentiate between various components, especially when it comes to safety, functionality, and compliance with industry standards. Two commonly used terms are often interchanged: tanks and pressure vessels. While they share similarities, they serve distinct purposes and have unique characteristics. In this article, we’ll delve into the fundamental differences between a tank and a pressure vessel.
Understanding Tanks
A tank, in the context of industrial applications, refers to a container designed primarily for the storage of liquids or gases. Tanks are ubiquitous and can be found in various industries, including chemical, oil and gas, food and beverage, and water treatment. Here are some key characteristics of tanks:
- Storage Capacity: Tanks are primarily used to store substances, such as crude oil, water, chemicals, or liquefied gases, for extended periods.
- Low Pressure: Tanks generally operate at atmospheric pressure or low pressures, making them suitable for substances that don’t require high-pressure containment.
- Minimal Structural Requirements: Tanks are typically simple in design and have relatively lower structural requirements compared to pressure vessels.
- Limited Reinforcement: The walls of tanks may not require the same level of reinforcement as pressure vessels since they don’t endure high internal pressures.
- Various Shapes and Sizes: Tanks come in diverse shapes and sizes, allowing for customization based on the specific storage requirements.
Understanding Pressure Vessels
Pressure vessels are engineered containers that hold substances under high pressure or at specific temperatures. Industries such as petrochemical, pharmaceutical, aerospace, and power generation rely heavily on them. Below are the key characteristics of pressure vessels:
- High Pressure: Pressure vessels withstand substantial internal pressure, often exceeding atmospheric levels. Engineers design them specifically for this task.
- Complex Design: Compared to tanks, pressure vessels feature more intricate designs. They include thick walls, reinforcements, and built-in safety features to maintain integrity under stress.
- Critical Safety Standards: Due to the high-pressure environment, manufacturers adhere to strict safety regulations and conduct regular inspections to avoid catastrophic failures.
- Varied Applications: Engineers use pressure vessels in controlled processes like chemical reactions, steam generation, and high-pressure gas storage.
- Specific Shapes: Designers often shape pressure vessels as cylinders or spheres to distribute stress evenly, which boosts structural integrity.
Key Differences Between Tanks and Pressure Vessels
- Purpose: Tanks primarily store substances, while pressure vessels contain materials under high pressure or temperature.
- Operating Pressure: Tanks operate at low or atmospheric pressures. In contrast, pressure vessels manage high internal pressures.
- Complexity: Engineers design pressure vessels with more complexity than tanks. These vessels feature thicker walls, reinforcements, and built-in safety components.
- Regulations: Due to high-pressure operation, pressure vessels must meet strict safety regulations and undergo regular inspections. Tanks usually have fewer regulatory requirements.
- Applications: Tanks serve as storage units. Meanwhile, pressure vessels play a critical role in high-pressure processes like chemical reactions or energy generation.
In summary, tanks and pressure vessels are both crucial to industrial operations, but they serve different purposes and follow different standards. Understanding these differences helps you maintain safety, meet industry regulations, and optimize your processes. Whether you need storage or high-pressure containment, choosing the right equipment ensures your operation runs efficiently.
Selecting the Right Equipment
When choosing between a tank and a pressure vessel, considerations your application’s specific needs. Here are some key points:
- Pressure Requirements: First, determine the pressure your substance needs to be contained at. For high-pressure use, choose a pressure vessel; otherwise, a tank might be sufficient.
- Safety Regulations: Understand the safety regulations that apply to your industry. Pressure vessels demand higher compliance due to the risks involved.
- Material Compatibility: Check whether the material of the container suits the substance you’ll store. Some substances cause corrosion or react negatively with certain materials.
- Volume and Space Constraints: Assess your available space. Tanks often offer more customization, while pressure vessels may face limitations due to their design.
- Lifecycle Cost: Evaluate both initial and long-term costs. Pressure vessels usually come with higher upfront and maintenance costs than tanks.
- Process Conditions: Consider your operating environment. If your process needs precise pressure or temperature control, a pressure vessel is typically the better choice.
- Consult with Experts: If unsure, talk to engineers or equipment experts. They can guide you toward the safest and most cost-effective solution.
Maintenance and Safety
Once you’ve selected the right equipment, you need to maintain it properly to ensure safety and long-term performance.
Tanks:
- Regular Inspection: Even though tanks operate at low pressure, you still need to schedule regular inspections to check for leaks, corrosion, or structural issues.
- Corrosion Protection: Apply coatings, linings, or cathodic protection systems to minimize corrosion, based on the tank’s material and what it stores.
- Leak Detection: Install leak detection systems to catch and fix leaks quickly. This step is vital for preventing hazards and environmental damage.
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in storage tanks to reduce the risk of harmful gas or fume buildup.
- Emergency Response Plan: Create a detailed emergency plan for leaks, spills, or other incidents. A quick, coordinated response helps reduce harm and operational downtime.
Pressure Vessels:
- Scheduled Inspections: Pressure vessels undergo more rigorous inspections, often with non-destructive testing. Follow industry-specific standards and schedule checks regularly.
- Pressure Relief Devices: Install and maintain relief devices to prevent over-pressurization, which can cause catastrophic failure.
- Material Integrity: Monitor material condition over time to ensure it can withstand high-pressure environments.
- Safety Valves: Calibrate and test safety valves routinely to ensure they function correctly and release pressure when necessary.
- Operator Training: Train personnel thoroughly on safety protocols, proper usage, and emergency procedures for pressure vessels.
Compliance and Documentation:
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of inspections, maintenance activities, repairs, and any modifications made to your tanks or pressure vessels. This documentation is critical for regulatory compliance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay updated with the latest industry and safety regulations. Ensure that your equipment complies with these standards, and be prepared for inspections by regulatory authorities.
- Emergency Response Plans: Regularly review and update emergency response plans, and conduct drills to ensure that your team is well-prepared for any unforeseen incidents.
- Tanks are primarily designed for the storage of liquids or gases at low pressures, offering flexibility in terms of size and shape. They are simpler in design and often have fewer regulatory requirements.
- Pressure vessels, on the other hand, are engineered to withstand high pressures and specific temperature conditions. They are more complex in design, subject to rigorous safety regulations, and are commonly used in critical processes.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the fields of tanks and pressure vessels are not immune to innovation. It’s crucial to stay informed about emerging trends and technologies that can enhance the performance, safety, and sustainability of these essential industrial components:
Tanks:
- Smart Tank Monitoring: IoT (Internet of Things) technology is being integrated into tanks to enable real-time monitoring of liquid levels, temperature, and other parameters. This helps in optimizing storage and ensuring timely refills or maintenance.
- Composite Materials: Tanks made from advanced composite materials are becoming more popular due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. They are especially valuable in industries where corrosion is a concern.
- Sustainability: Green technologies are increasingly being incorporated into tank design. Rainwater harvesting tanks and environmentally friendly coatings are examples of sustainable solutions.
Pressure Vessels:
- Advanced Materials: Innovations in materials science are leading to the development of stronger, more corrosion-resistant materials for pressure vessel construction, improving both safety and longevity.
- Digital Twins: Digital twin technology is being used to create virtual replicas of pressure vessels, allowing for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and risks.
- Nanotechnology: Nanomaterials and coatings are being explored for pressure vessels to enhance their strength and resistance to wear, leading to improved performance and safety.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): This technology is starting to find applications in pressure vessel fabrication, allowing for complex geometries and customized designs while maintaining structural integrity.
- Hydrogen Storage: As the demand for hydrogen as a clean energy source grows, there is a focus on developing pressure vessels capable of safely storing and transporting hydrogen at high pressures.
Sustainability and Safety:
- Energy Efficiency: Manufacturers are working on designs that minimize energy consumption, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- Safety Measures: Continuous improvements in safety features, such as advanced pressure relief systems and real-time monitoring, are crucial for preventing accidents.
- Environmental Compliance: With increasing environmental regulations, there’s a growing emphasis on ensuring that tanks and pressure vessels are in compliance with emissions and pollution control standards.
- Circular Economy: Designing equipment with an eye toward recycling and reusing materials is gaining importance as part of sustainability efforts.
The world of tanks and pressure vessels is dynamic and constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of various industries. Understanding the fundamental differences between these components, along with the latest trends and innovations, is essential for making informed decisions, ensuring safety, and optimizing industrial processes.
As you navigate the complexities of choosing, maintaining, and utilizing tanks or pressure vessels in your operations, keep in mind the following key takeaways:
- Purpose Matters: Always consider the specific purpose of your equipment. Tanks are for storage, while pressure vessels are for high-pressure applications. Choosing the right one is crucial.
- Safety First: Prioritize safety above all else. Both tanks and pressure vessels can pose risks if not properly maintained or operated. Adhere to strict safety protocols and compliance with regulations.
- Regular Maintenance: Establish and adhere to a rigorous maintenance schedule for your equipment. This will not only extend their lifespan but also enhance their safety and efficiency.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest industry trends and innovations. Emerging technologies can offer opportunities for improved performance, efficiency, and sustainability.
- Environmental Responsibility: Consider the environmental impact of your equipment choices. Sustainable materials and practices are becoming increasingly important in industrial settings.
- Consult Experts: When in doubt, seek guidance from experts and engineers who specialize in tanks and pressure vessels. Their expertise can help you make informed decisions and navigate complex regulations.
By following these principles and embracing technological advancements, you can ensure that your tanks and pressure vessels remain assets that contribute to the success and sustainability of your industrial operations.
Need a reliable partner?
FAQ: Understanding the Difference Between a Tank and a Pressure Vessel
What defines a tank and a pressure vessel, and how do they differ?
A tank is a storage unit designed to hold liquids, gases, or solids without significant internal pressure differences from the external environment. Tanks are often cylindrical or have simple shapes and are used in a wide range of applications, from water storage to holding fuel. On the other hand, a pressure vessel is engineered to hold fluids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure. These vessels can be found in industries like chemical processing, oil and gas, and power generation, where managing high-pressure conditions is crucial. The key difference lies in the design and construction standards to safely withstand the internal pressure.
Why are pressure vessels subject to stricter regulations than tanks?
Due to the potential risks associated with the high-pressure conditions, pressure vessels are subject to stricter regulations and standards to ensure safety and prevent accidents. These regulations cover the design, construction, testing, and maintenance of pressure vessels. Standards such as the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code in the United States are internationally recognized for ensuring the integrity and safety of these vessels. Tanks, while also regulated, do not typically operate under the same high-pressure conditions and thus have less stringent requirements.
Can a tank become a pressure vessel under certain conditions?
Yes, a tank can become a pressure vessel if it is modified or used in a way that subjects it to internal pressures significantly above atmospheric pressure. This can happen intentionally or unintentionally, through processes that generate pressure inside the tank. When a tank is used in such a manner, it must be evaluated and possibly redesigned to meet the safety standards and regulations applicable to pressure vessels.
What materials are commonly used to construct pressure vessels, and how do they compare to those used for tanks?
Pressure vessels are typically made from materials capable of withstanding high pressures, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys designed for specific applications and chemical resistances. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and ability to maintain integrity under pressure. Tanks, while also made from durable materials like steel, fiberglass, and plastic, do not require the same level of strength and pressure resistance. The material choice for tanks often focuses more on the chemical compatibility with the stored substance and cost-effectiveness.
How do maintenance and inspection requirements differ between tanks and pressure vessels?
Maintenance and inspection of pressure vessels are more rigorous and frequent due to the potential hazards associated with failure. Regular inspections are mandated by safety regulations, focusing on detecting signs of wear, corrosion, and potential failure points. Pressure vessels may also require periodic testing to verify their integrity under operating conditions. Tanks, while also needing regular maintenance and inspection, typically have less stringent requirements. The focus for tanks is often on preventing leaks and ensuring the stored material does not contaminate or degrade the tank material.
Table of Contents
ToggleRelated Blog Post
- Is water tank a pressure vessel?
- Is a water heater a pressure vessel?
- What is the purpose of a pressure vessel?
- Should a pressure vessel have water in it?
- At what pressure does a tank become a pressure vessel?
- Is a compressed air tank considered a pressure vessel?
- Is air receiver tank a pressure vessel?
- What are the three types of pressure tanks?
- What is a pressure vessel for domestic water?
- Why would I need a pressure tank?
- Is a blowdown tank a pressure vessel?
Need Action?
We are here to make it happen. Request a qoute!
Solutions
In the realm of industrial solutions, Red River emerges as a pioneer, offering a diverse range of custom-engineered products and facilities. Among our specialties is the design and production of Custom/OEM Pressure Vessels, meticulously crafted to meet individual client requirements, ensuring performance under various pressure conditions. Our expertise extends to the domain of prefabrication, where Red River leads with distinction.
The company excels in creating prefabricated facilities, modules, and packages, reinforcing its stance as a forerunner in innovation and quality. This proficiency is further mirrored in their Modular Skids offering, where they provide an array of Modular Fabricated Skid Packages and Packaged equipment. Each piece is tailored to client specifications, underlining their commitment to delivering precision and excellence in every project they undertake.
Need action? Ready to Get Started?
We are here to make it happen. Request a qoute!