
Table of Contents
Toggle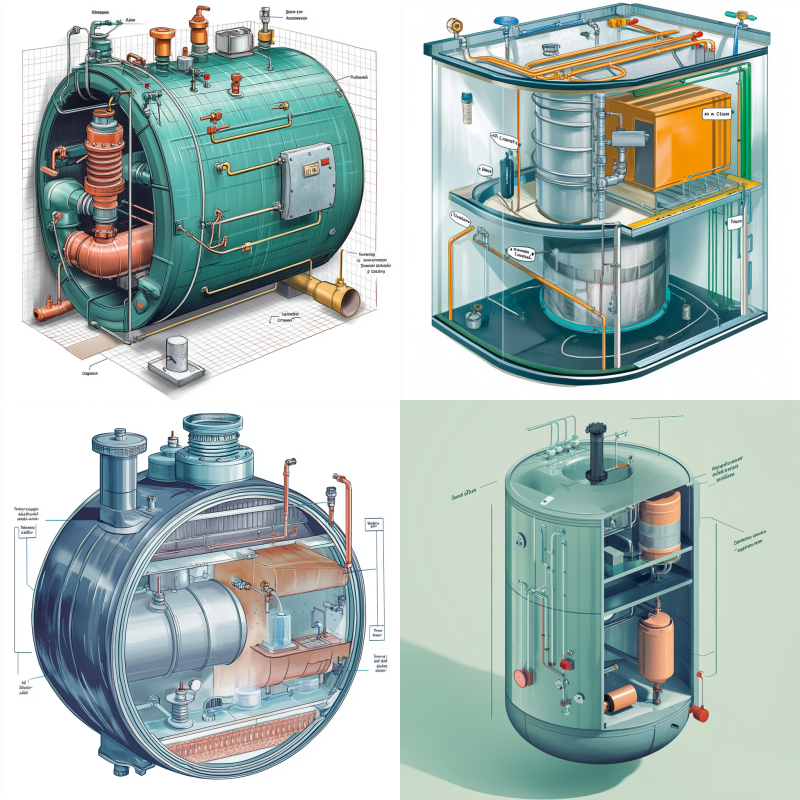
If you’re maintaining a home heating or boiler system, understanding the role of the expansion tank (also known as an expansion vessel) is crucial. One of the key aspects of ensuring the smooth operation of your system is knowing how to check expansion tank pressure. This guide will walk you through the process, explain why it’s important, and provide tips for troubleshooting your expansion tank pressure effectively.
An expansion tank is a small but essential component in sealed heating systems like boilers and central heating setups. When water in your heating system heats up, it expands. Because water cannot compress, this expansion increases the pressure within your system. Without an expansion tank, this pressure could cause significant damage, including leaks, burst pipes, or component failure.
The expansion tank works by providing a space for the water to expand into. It has two chambers: one filled with water and the other with air, separated by a flexible membrane or diaphragm. As water heats up and expands, the air cushion absorbs the pressure increase, keeping the system safe and functioning smoothly.
If your expansion tank’s air chamber is not properly pressurized, your system can face issues like pressure spikes, leaks, and even system shutdowns. How to check expansion tank pressure is an important skill for anyone maintaining a heating system. If the pressure is too low or the air cushion is compromised, it could lead to inefficient operation, damage, and costly repairs.
There are a few common signs that your expansion tank may need attention:
Frequent pressure drops: If the system pressure fluctuates regularly, it may indicate an issue with the expansion tank.
Pressure relief valve activation: If the pressure relief valve constantly releases water, the expansion tank could be full of water or improperly pressurized.
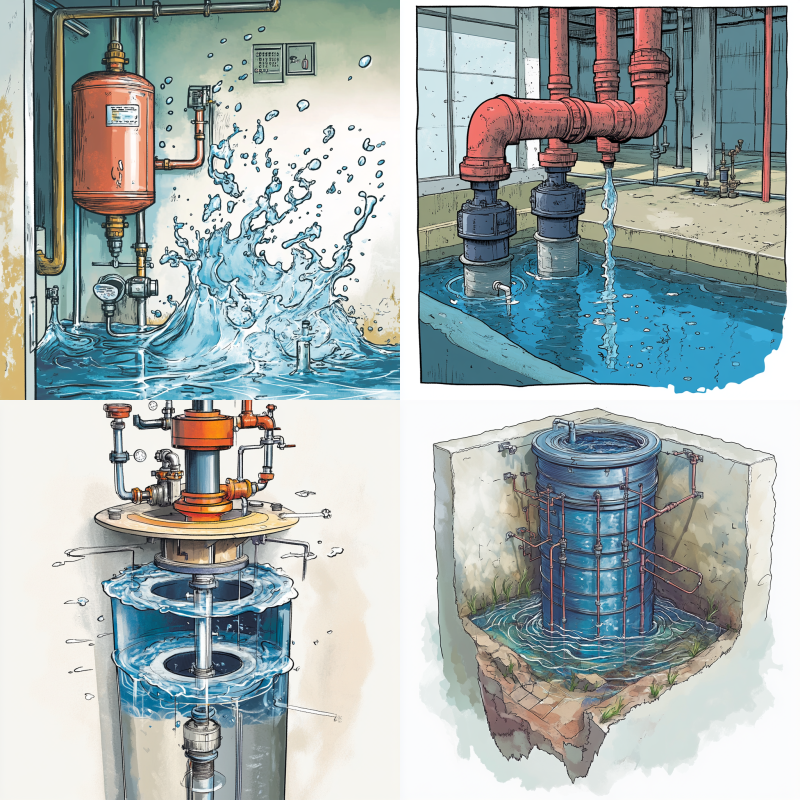
Water from the air valve: When you press the valve pin, if water, rather than air, comes out, this is a clear sign of a waterlogged tank.
Unusual noises: Banging or gurgling sounds in the pipes could suggest that the expansion tank isn’t functioning properly.
Visible leaks or system shutdowns: If you notice leaks or the boiler shuts down frequently due to pressure issues, the expansion tank may be malfunctioning.
You can find more information about diagnosing expansion tank problems in our guide on Signs of a Faulty Expansion Vessel.
Maintaining the correct air pressure in your expansion tank is essential for preventing pressure spikes within your heating system. When the tank is full of water or the air pressure is too low, it cannot absorb pressure changes effectively. This can lead to:
Pressure spikes: Without the air cushion, pressure can rise quickly, triggering frequent activation of the pressure relief valve.
Leaks and pipe bursts: Excessive pressure stresses pipes and joints, leading to leaks or even bursts.
System inefficiency: A waterlogged expansion tank or incorrect pressure causes your system to shut down or malfunction frequently.
Premature failure of components: Continuous pressure fluctuations can wear out components like pumps, valves, and the boiler itself, reducing their lifespan.
Regular maintenance, including checking the expansion tank pressure, is key to ensuring your heating system operates efficiently and avoids costly repairs.
For more information on what happens when there’s too much pressure inside the boiler, take a look at our post on the risks of excessive pressure in boilers.
Regularly checking your expansion tank pressure is a crucial part of heating system maintenance. By understanding how to check expansion tank pressure and knowing the signs of malfunction, you can keep your system running smoothly, avoid expensive repairs, and extend the lifespan of your boiler and heating components.
Don’t neglect this vital part of your heating system schedule an inspection and ensure your expansion tank is in optimal condition today!
For more tips, check out our comprehensive guide on should an expansion vessel be full of water.
Red River specializes in the design and manufacturing of pressure vessels. We also fabricate related items such as prefabricated spools and skid packages.
Reach out to us today and experience the Red River difference. Where American-made products and American Values come together, we care more
Simply press the valve pin to release a small amount of water. If water comes out, your expansion tank is full of water. Then, use a tire pressure gauge to check the air side of the tank.
When an expansion tank is full of water, it means the air chamber has been compromised, usually due to a damaged diaphragm. This prevents the tank from absorbing pressure changes, leading to system problems.
It’s best to check your expansion tank pressure once a year, ideally during your annual boiler service.
If the tank fails, pressure in your heating system will spike, causing leaks, frequent pressure relief valve activation, or even system shutdown.
In some cases, repressurizing the air side can fix the issue, but if the membrane is damaged, replacement is necessary. Professional help is recommended.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn the realm of industrial solutions, Red River emerges as a pioneer, offering a diverse range of custom-engineered products and facilities. Among our specialties is the design and production of Custom/OEM Pressure Vessels, meticulously crafted to meet individual client requirements, ensuring performance under various pressure conditions. Our expertise extends to the domain of prefabrication, where Red River leads with distinction.
The company excels in creating prefabricated facilities, modules, and packages, reinforcing its stance as a forerunner in innovation and quality. This proficiency is further mirrored in their Modular Skids offering, where they provide an array of Modular Fabricated Skid Packages and Packaged equipment. Each piece is tailored to client specifications, underlining their commitment to delivering precision and excellence in every project they undertake.